QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
ISO 9001 certification is the internationally recognized standard for quality management systems. This standard helps companies consistently provide high quality products that meet their consumers’ expectations while also fulfilling any regulatory requirements. Although certification is not a legal requirement, it demonstrates a company’s dedication to the continuous improvement in its processes and product quality.
All ISO standards are reviewed every five years; however, revisions are only made when the information isn’t relevant for the current marketplace. ISO 9001:2015 places a greater importance on risk and includes an updated structure compatible with other management system standards. Following is a breakdown of these key differences.
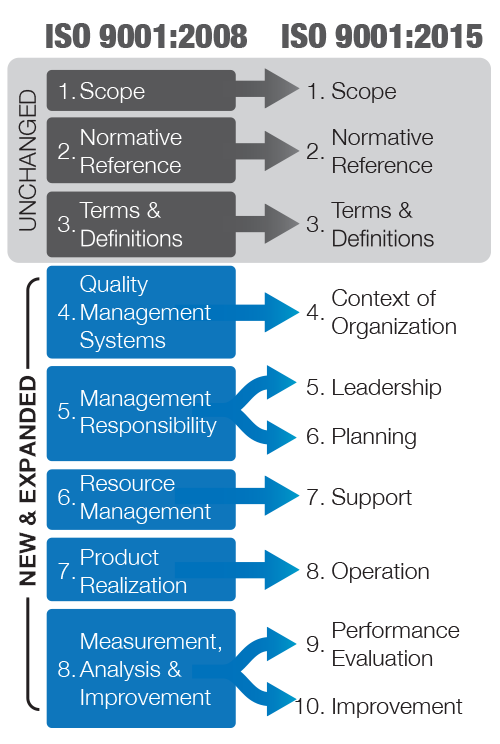
NEW & EXPANDED CLAUSES
The updated standard includes ten clauses. While the first three clauses have remained the same, clauses four through 10 now have the same structure as other ISO standards, known as the High-Level Structure. This revision makes it easier for organizations who use multiple management systems.
The “New & Expanded” section in the chart shows how the clauses have been revised. “Management Responsibility” is broken into “Leadership” and “Planning,” and “Measurement, Analysis & Improvement” is now two separate sections.
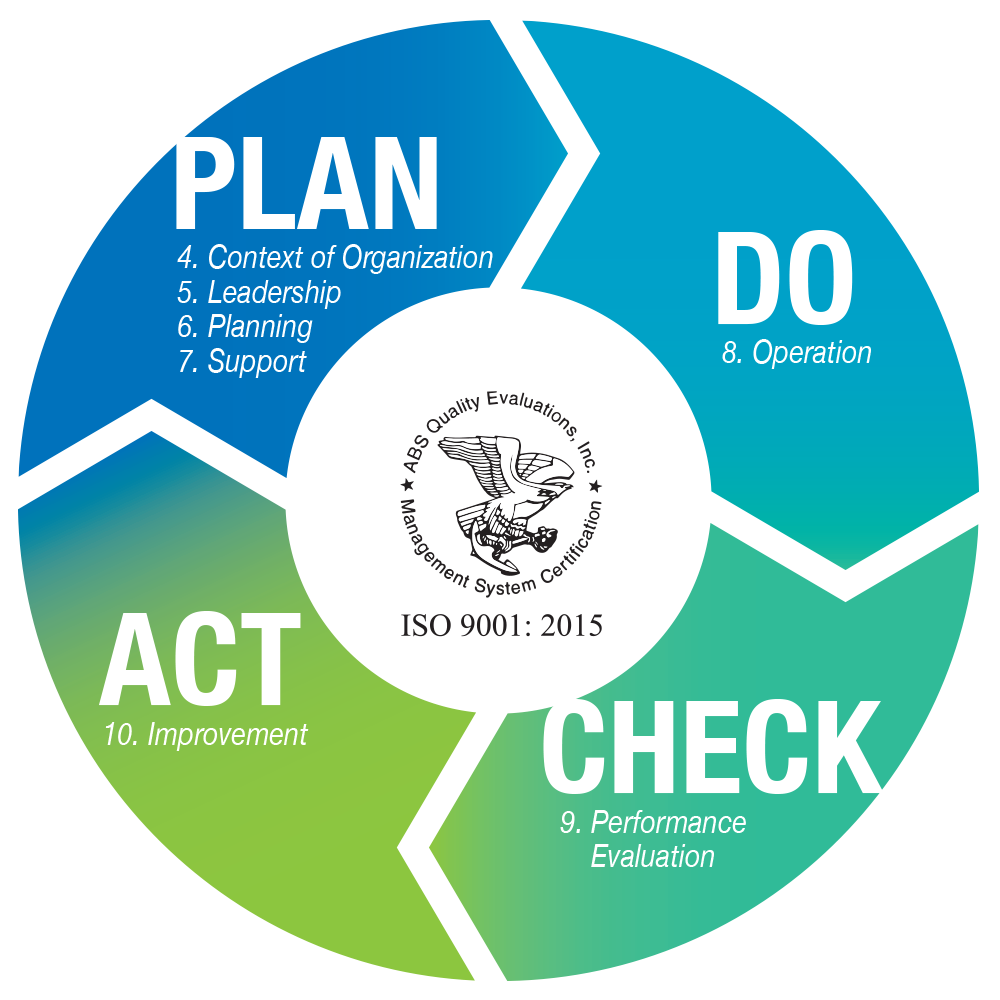
PDCA CYCLE
The last seven clauses are now arranged according to the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) cycle. This continuous four-stage model is used to promote systematic improvement within organizations.
RISK-BASED THINKING
ISO 9001:2015 encourages risk-based thinking to help companies identify unexpected circumstances, including how a company's inputs and outputs affect the production process. For example, a manufacturer must consider how its suppliers (inputs) and purchasers (outputs) affect its ability to do business. By regularly performing risk analysis, companies can determine weak points and opportunities.